Avi Loeb’s Latest 3I/ATLAS THEORY: It’s INTERESTED in JUPITER
Renowned astrophysicist Avi Loeb has recently put forth a captivating theory regarding the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS, proposing that it may have a specific interest in Jupiter. This hypothesis has sparked significant discussions within the scientific community, as it challenges conventional views about the behavior of interstellar objects and their interactions with planets in our solar system.
Understanding 3I/ATLAS
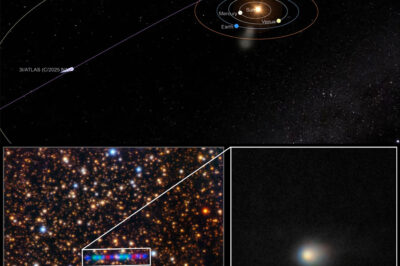
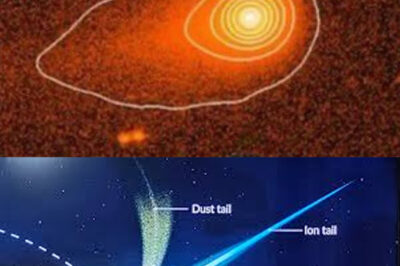
Discovered in July 2025, 3I/ATLAS is classified as an interstellar comet that originated from outside our solar system. Unlike typical comets that follow predictable orbits around the Sun, 3I/ATLAS is on a hyperbolic trajectory, indicating that it will pass through our solar system only once before continuing its journey into the vastness of interstellar space. As it approached the Sun, anticipation grew among astronomers eager to study its behavior and characteristics, particularly its unusual tail, which appeared to exhibit propulsion-like features rather than the typical dust emissions associated with comets.
The initial observations of 3I/ATLAS were intriguing, as scientists noted its unusual tail structure and brightness. These characteristics led to speculation about the object’s composition and the processes influencing its behavior. As the comet neared perihelion—the point at which it was closest to the Sun—scientists prepared to gather extensive data to analyze its interactions with solar radiation and gravitational forces.
The New Theory: Interest in Jupiter
Avi Loeb’s latest theory posits that 3I/ATLAS may be drawn to Jupiter due to the planet’s immense gravitational influence and its potential as a site for further exploration. Here are some key points that form the basis of his hypothesis:
-
Gravitational Interactions: Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system, possessing a strong gravitational pull that can significantly influence the trajectories of nearby celestial objects. Loeb suggests that 3I/ATLAS could be utilizing Jupiter’s gravity to alter its path, potentially as a means of gaining speed or redirecting its trajectory as it travels through the solar system. This gravitational assist could allow the comet to navigate its journey more efficiently, taking advantage of the dynamics of the solar system.
Potential for Exploration: Beyond gravitational assistance, Loeb speculates that 3I/ATLAS might be interested in Jupiter for the scientific opportunities the planet presents. Jupiter’s complex atmosphere, magnetic field, and numerous moons—especially the icy worlds like Europa and Ganymede—make it a fascinating target for exploration. Loeb raises the possibility that 3I/ATLAS could be gathering data or even sending signals back to its origin point, suggesting a level of sophistication that challenges our understanding of interstellar objects.
Comparison to Other Interstellar Objects: Loeb draws parallels between 3I/ATLAS and other interstellar objects, such as ‘Oumuamua, which exhibited unusual behavior as it passed through our solar system. Just as ‘Oumuamua sparked discussions about the potential for artificial origins, 3I/ATLAS’s trajectory and behavior may indicate a higher level of intention or purpose. This perspective encourages scientists to consider the possibility that interstellar objects could have motivations beyond mere chance encounters with our solar system.
Implications of the Theory
Loeb’s theory has significant implications for our understanding of interstellar objects and their interactions with the solar system:
-
Reevaluation of Interstellar Objects: If 3I/ATLAS is indeed exhibiting behaviors indicative of intentionality or interest in Jupiter, it could necessitate a reevaluation of how scientists approach the study of interstellar objects. This would involve considering the potential for complex interactions and motivations behind their trajectories, prompting researchers to explore new models and frameworks for understanding these celestial bodies.
Encouragement for Further Research: Loeb’s hypothesis emphasizes the need for further observational studies of 3I/ATLAS and other interstellar objects. Understanding their behavior, composition, and interactions with celestial bodies like Jupiter could yield valuable insights into the dynamics of our solar system and the broader universe. Such research could also inform future missions aimed at exploring the outer planets and their moons.
Public Interest and Speculation: The idea that an interstellar object might be interested in a planet within our solar system captures the public’s imagination. This theory has the potential to inspire further interest in astronomy and space exploration, encouraging a new generation of scientists and enthusiasts to engage with these fascinating topics. The prospect of studying interstellar objects with intentionality adds an exciting dimension to our understanding of the cosmos.

Conclusion
Avi Loeb’s latest theory regarding 3I/ATLAS and its potential interest in Jupiter invites us to rethink our understanding of interstellar objects and their interactions with our solar system. By considering the gravitational influence of Jupiter and the scientific opportunities it presents, Loeb challenges conventional views and opens new avenues for exploration.
As researchers continue to study 3I/ATLAS and similar interstellar bodies, the implications of this theory could lead to groundbreaking discoveries about the nature of our universe. The quest to understand these cosmic wanderers not only enhances our knowledge of interstellar phenomena but also fuels our curiosity about the possibilities that lie beyond our solar system. As we look to the stars, theories like Loeb’s remind us of the dynamic and interconnected nature of the cosmos, urging us to remain vigilant in our exploration of the unknown.
News
On December 15th, 2025, Interstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Will Safely Pass by Earth at a Distance of Several Million Kilometers, Offering a Unique Opportunity for Scientific Observation and Public Engagement Without Any Threat or Physical Impact on Our Planet, Inspiring Interest in Astronomy and Space Exploration
What Will 3I/ATLAS Do to Earth on December 15th? As December 15th, 2025, approaches, the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS is set…
The Explosion of Interstellar Object 3I/ATLAS at Perihelion Shocks Scientists and Raises Profound Questions About the Nature of Comets, Challenging Existing Models of Interstellar Bodies, Offering New Opportunities for Discovering Cosmic Materials, and Highlighting the Need for Enhanced Collaborative Research in Understanding the Dynamic and Unpredictable Universe
INTERSTELLAR OBJECT 3I/ATLAS Has Exploded at Perihelion – And Scientists Are SHOCKED In a dramatic and unexpected turn of events,…
NASA’s Revelation That 3I/ATLAS’s Tail Exhibits Propulsion-Like Characteristics Rather Than Typical Dust Emissions Sparks Intrigue and Debate Among Scientists, Raising Profound Questions About the Nature, Origins, and Potential Artificial Mechanisms of This Interstellar Object and Its Implications for Our Understanding of the Universe and Extraterrestrial Life
NASA Admits 3I/ATLAS’s TAIL Looks More Like PROPULSION Than Dust In a stunning revelation, NASA has confirmed that the tail…
MICHIO KAKU Explains Why 3I/ATLAS is Causing Panic Among Scientists Due to Its Unpredictable Trajectory, Potential for Extraterrestrial Life, Existential Risks, and Ethical Considerations Surrounding the Discovery of This Interstellar Object and Its Implications for Humanity’s Understanding of Life Beyond Earth
MICHIO KAKU: “Why 3I/ATLAS is Causing Panic Among SCIENTISTS” The interstellar object known as 3I/ATLAS has recently emerged as a…
JAMES WEBB TELESCOPE SHOCKS THE WORLD with a Discovery of Complex Organic Compounds and Possible Signals of Intelligent Life, Raising Profound Questions About Humanity’s Place in the Universe and Its Future in the Face of Potential Extraterrestrial Encounters
JAMES WEBB TELESCOPE SHOCKS THE WORLD: A Discovery So FRIGHTENING It Could ALTER THE FUTURE of HUMANITY FOREVER In an…
What to Expect from 3I/ATLAS as It Approaches Earth on December 15, 2025: Key Details About Its Close Pass, Scientific Observations, and the Assurance That This Interstellar Object Poses No Threat to Our Planet Despite Public Speculation and Interest in Its Unique Origins
What Will 3I/ATLAS Do to Earth on December 15th, 2025? The interstellar object known as 3I/ATLAS has captured the attention…
End of content
No more pages to load